Badge Cloning
& RFID Attacks for Physical Access

TRAVIS WEATHERS
BOLO

Echelon Risk + Cyber
Ralph May

Black Hills Information Security


Intended Audience & Purpose
-
Red Team Operators, Penetration Testers, Aspiring Physical Operators
- Folks who perform physical assessments but do not consider themselves RFID hackers
What's covered?
-
Common RFID technologies that we see most often as Physical Security Practitioners
-
Existing & New Tools that are readily available
-
TTPs that we've found to work and some that are a bad idea

AGENDA
RFID technologies
-
HID PROX (Common)
-
Indala (Rare)
-
EM (More Rare / Low Budget)
-
AWID (Extremely Rare / Expensive)
RFID Technologies:
UNEnCRYPTED 125kHz
These cards/readers leverage legacy technology that does not support encryption. This makes reading, writing, and emulating a breeze.
125kHz Readers

HID Slimeline
HID Mini Mullion


HID Wall Switch Keypad

RFID Technologies:
UNEnCRYPTED 125kHz (HID PROX)


Indala Proximity Mid-Range
Indala Proximity Classic
RFID Technologies:
UNEnCRYPTED 125kHz (Indala Proximity)




RFID Technologies:
UNEnCRYPTED 125kHz (em)




RFID Technologies:
UNEnCRYPTED 125kHz (AWID)

- HID iCLASS was intended to bridge the security shortfalls of PROX by adding encryption.
- In 2010, Milosch Meriac published a white paper titled "Heart of Darkness"
- Meriac was able to recover the master encryption/decryption keys that were embedded in all iCLASS readers. Making the technology cleanable, assuming that you have the keys.
RFID Technologies:
EnCRYPTED 13.56mHz (iclass Legacy)
13.56MHz iCLASS Legacy



RFID Technologies:
EnCRYPTED 13.56mHz (iclass Legacy)

- These technologies are still considered secure at the time of this writing.
- It is still possible to leverage these technologies to gain unauthorized access to a facility. Assuming that Standard keys are in place and not Elite keys.
- Standard Keys: Same concept as iCLASS legacy, except they have not yet been compromised.
- Elite Keys: Customer-specific keys; no two customers have the same key.
RFID Technologies:
EnCRYPTED 13.56mHz (iclass se)
13.56MHz iCLASS SE



RFID Technologies:
EnCRYPTED 13.56mHz (iclass se)

- These readers are designed to support various media types (e.g., cards, Bluetooth, etc.)
- Typically observed in building upgrades where various card types might be in active use
- Though they look the same, there are tons of variations
- Most common is the iCLASS (SE) with PROX/EM/AWID variant
- Cannot support PROX & Indala at the same time
RFID Technologies:
multiclass / multiclass se
13.56MHz & 125kHz




multiCLASS
multiCLASS SE
RFID Technologies:
multiclass / multiclass se

RFID Technologies:
multiclass se (Signo)
- Newest line of HID readers that can support all technologies in a single reader
13.56MHz & 125kHz

Biometric 25B
RFID Technologies:
multiclass se (Signo)





40 Series
Express
Enrollment
20 Series

equipment overview
iCLASS R90SE
- 13.56 Mhz
- iCLASS (Legacy)
- iCLASS SE
- SEOS
- MIFARE
- MIFARE DESfire EV1
- HID Mobile Access
MAXIPROX 5375
- All 125 kHz Prox Cards
- All Indala 125 kHz Cards
(Not so) longrange Badge cloning
Indala asr-620++




iCLASS R90SE
MAXIPROX 5375
(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning
Indala asr-620++

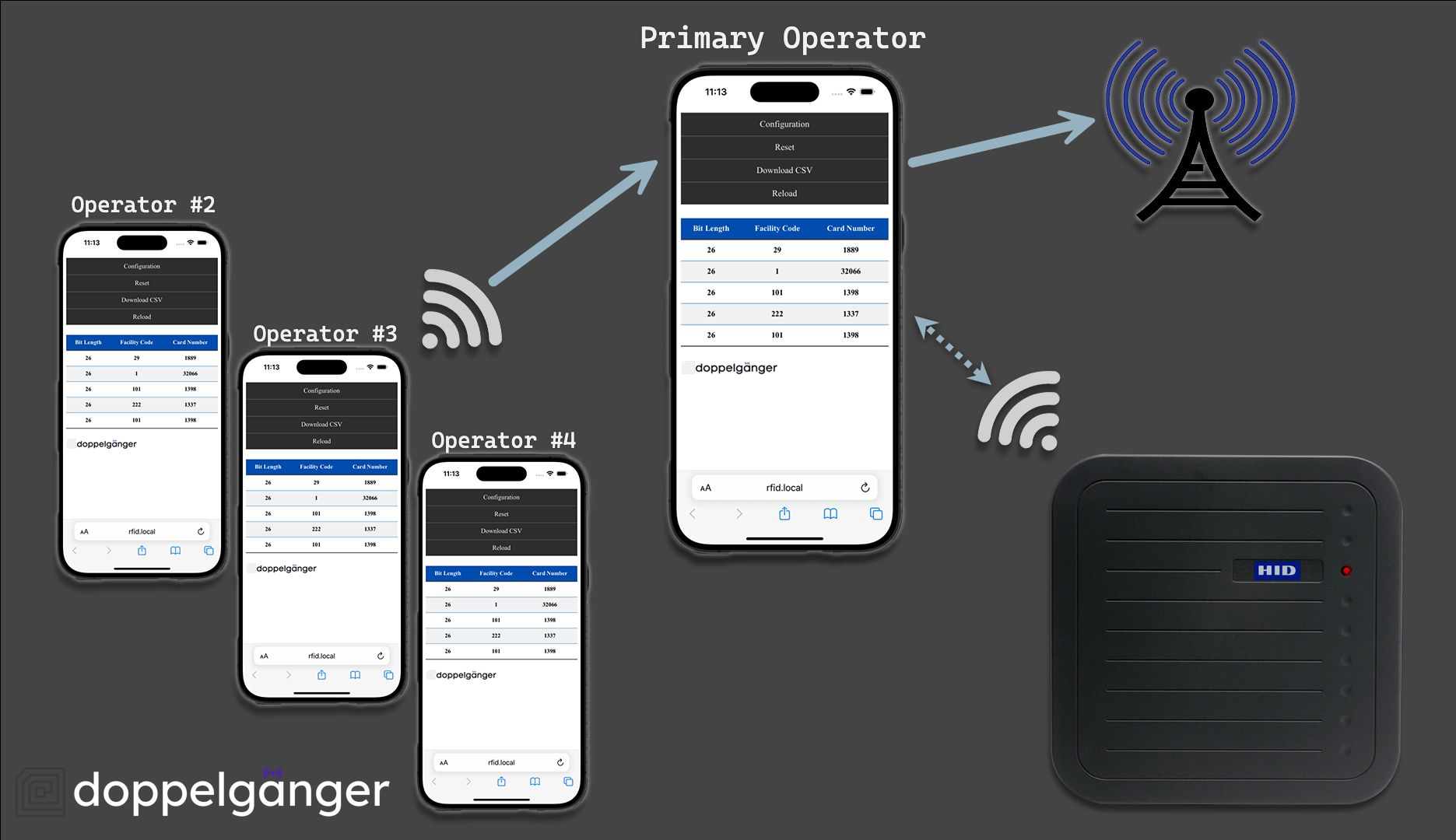
Doppelgänger
ESP32 Firmware
- Processes Wiegand Data
- Can Send Notifications
- Uses Phone's Hotspot
-
Actively Supported
(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning

(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning

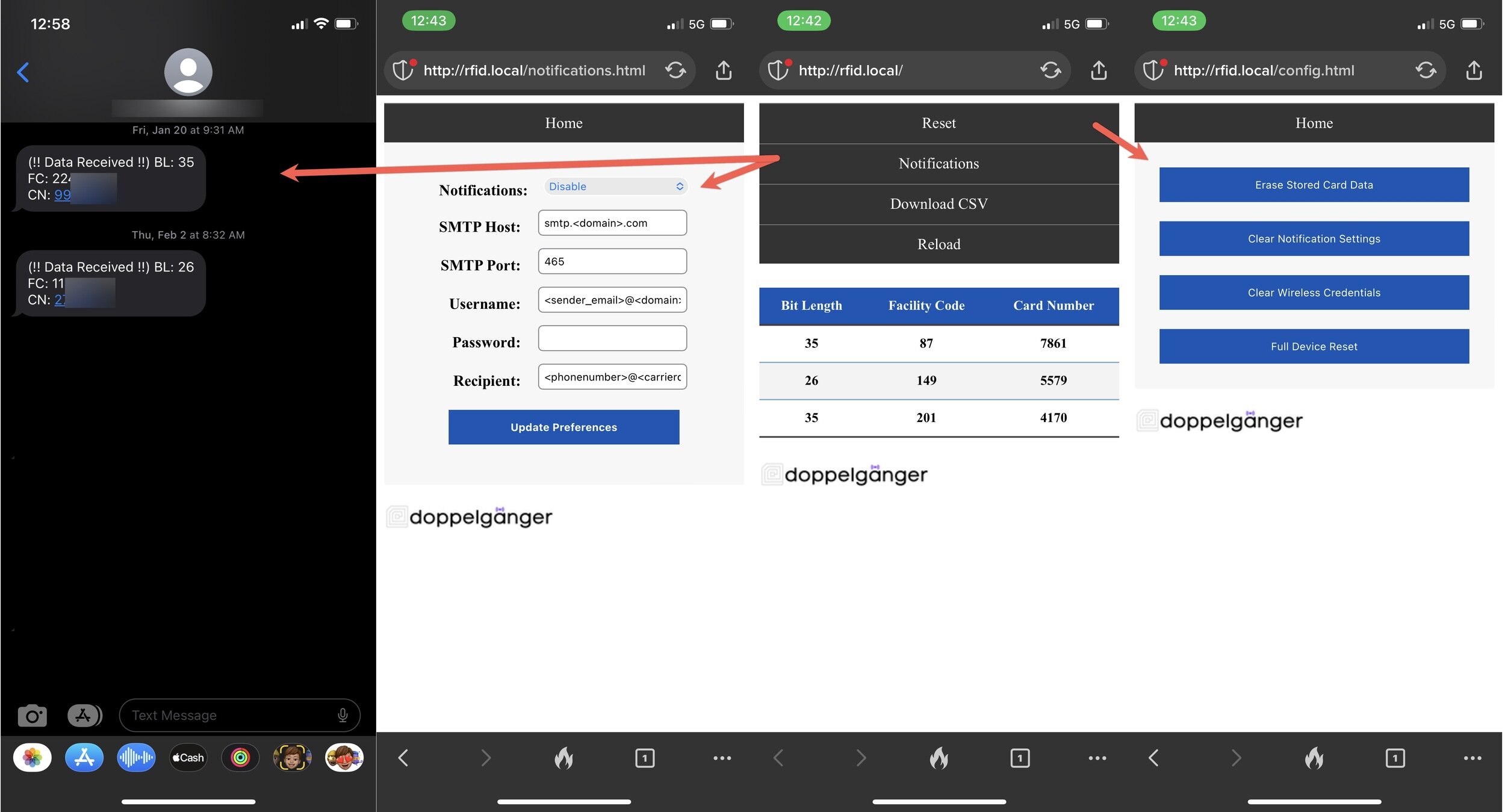
Doppelganger:
Connection & Notifications
Doppelganger:
Receiving Notifications
Doppelganger:
Device ReSET
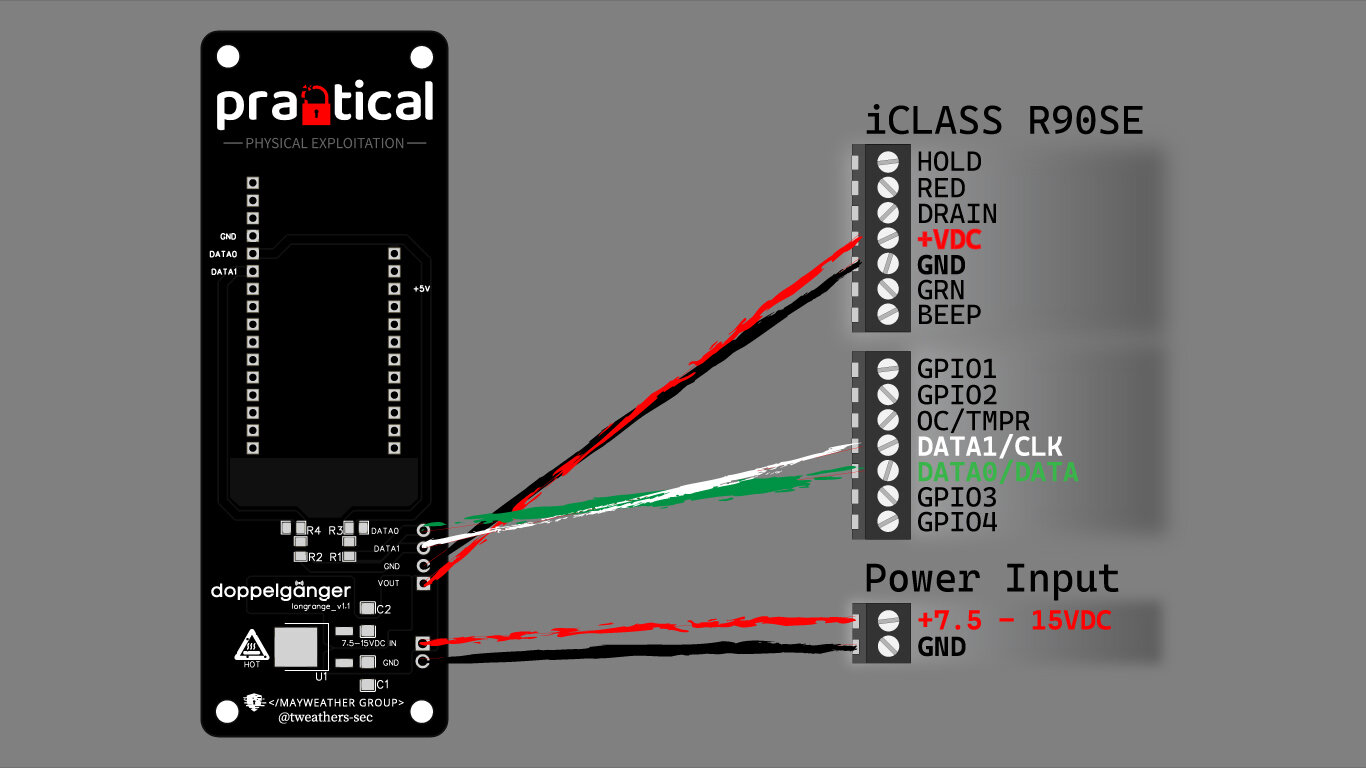
(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning
Wiring Diagram

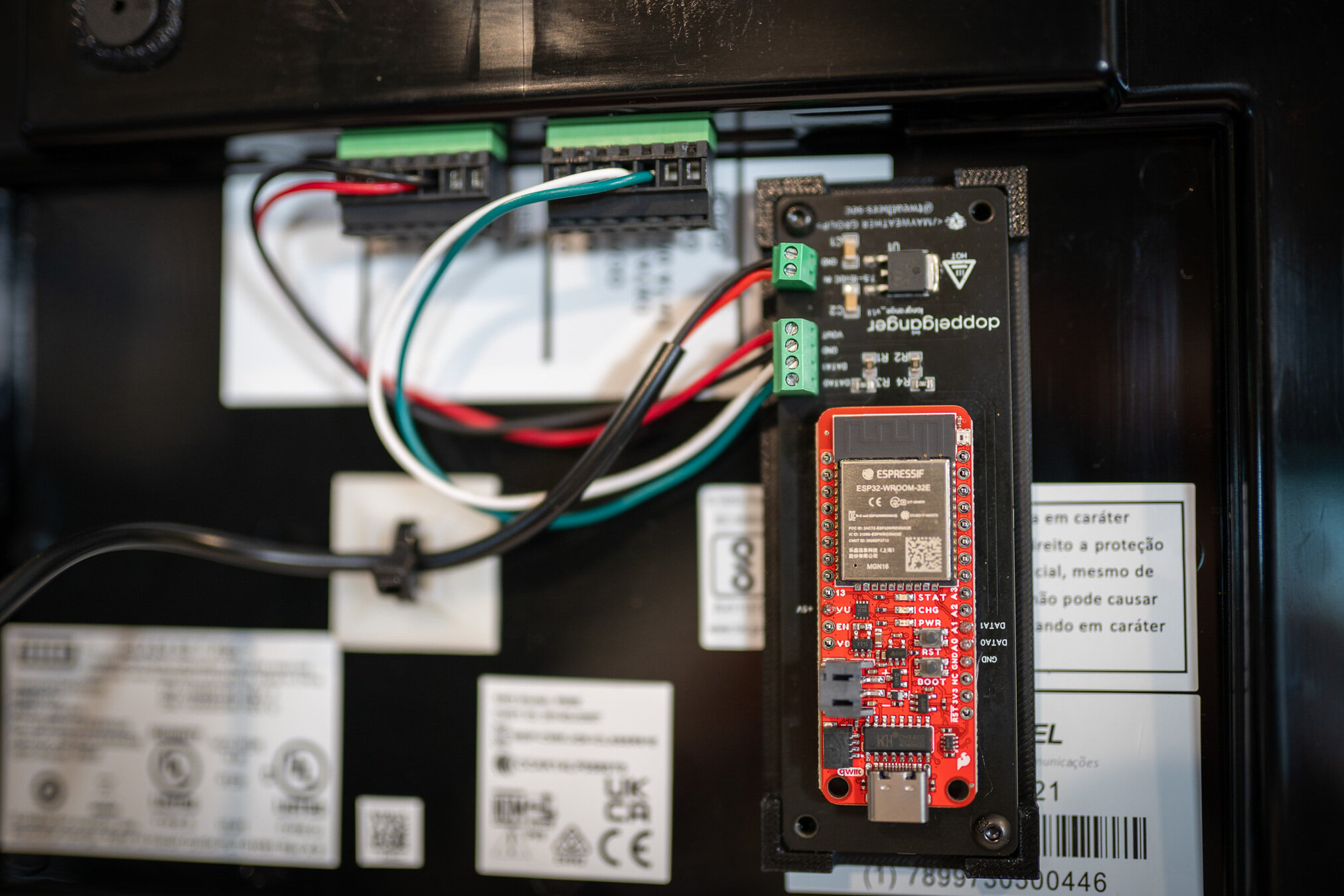
(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning
R90SE Installation



(Not so) longrange Badge Cloning
Briefcase
Backpack

multiCLASS SE
13.56 Mhz (High Frequency)
-
iCLASS SE
-
SEOS
-
iCLASS SR
-
iCLASS (Legacy)
-
SE for MIFARE Classic
-
SE for MIFARE DESFire EV1
125 kHz (Low Frequency)
-
HID AWID
-
EM4102
-
Prox Credentials
-
Can be flashed to convert to SIO-Enabled mode.
non-destructive Plant:
Stealth Wiegand Data Interpreter


multiCLASS SE
Keypad Equipped
- Captures and concatenates PIN entries
13.56 Mhz (High Frequency)
-
iCLASS SE
-
SEOS
-
iCLASS SR
-
iCLASS (Legacy)
-
SE for MIFARE Classic
-
SE for MIFARE DESFire EV1
125 kHz (Low Frequency)
-
HID AWID
-
EM4102
-
HID Prox Credentials
non-destructive Plant:
MFAS Wiegand Data Interpreter


RFID ATTACKS:
Stealth Wiegand Data Interpreter
Pros / Use Case
destructive IMPlant:
ESPKey / ESP RFID Tool
- Capture and replay data as needed to gain access.
- This process is akin to credential harvesting for physical access control systems.
- Vampire taps may inflict permanent damage on attached wires.
- A single misstep can lead to a severed wire, rendering the reader inoperable.
- Damage can transform a successful engagement into a strained client relationship.
- Even after a meticulous installation and removal, bare copper remains exposed.
- This exposure may result in deterioration or, in certain instances, wires shorting out.
Potential Issues

Tech Specs
- CPU SAM7S512
- Storage External 2MBits / 256Kb SPI flash
- Interface 4x power LEDs, 4x mode LEDs, 1x button.
- Performance
- LF (125KHz/134KHz): 70mm @ 65V
- HF (13.56MHz): 88mm @ 44V

Static Analysis:
Proxmark3 rdv4 [Active Support]
- Writing captured card data to blank cards
- Static analysis of cards & readers
- Emulation of card data (NOT RECOMMENDED)
- RFID Brute-forcing
Use Case

Known Issues
- Fragile
- Temperamental
- To use as Proxmark, must use Windows
- Proxmark3 Software w/screen (not maintained)
- Writing captured card data to blank cards
- Static analysis of cards & readers
- Emulation of card data (NOT RECOMMENDED)
- RFID Brute-forcing
Use Case


Static Analysis:
icopy-xs [Not Actively Supported]

Known Issues
- Expensive for it use case
- Flipper's draw attention from everyone
- Not capable of writing iCLASS credentials?
Static Analysis:
Flipper Zero w/NARD SAM Expansion
- Writing captured card data to blank cards
- Static analysis of cards & readers
- Emulation of card data (NOT RECOMMENDED)
- RFID Brute-forcing
Use Case
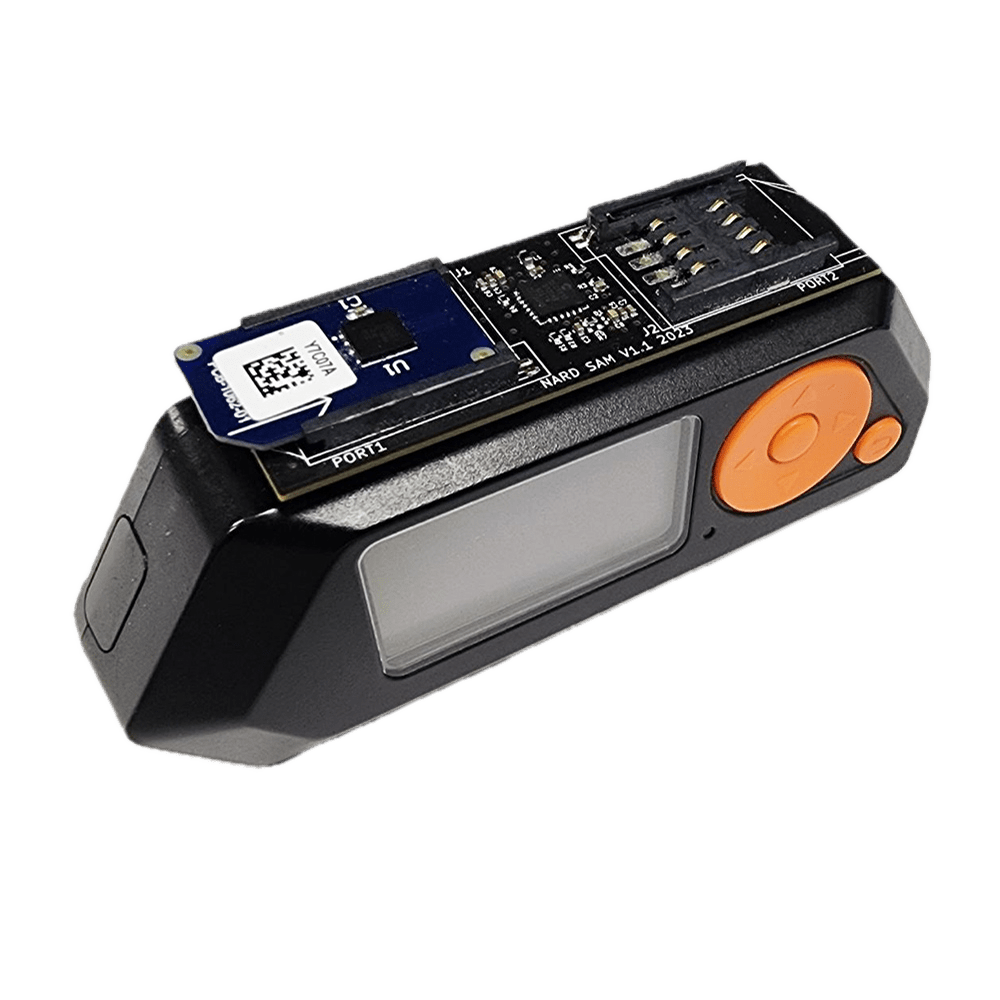

RFID Attacks
- Wiegand serves as the primary communication method for RFID readers and controllers.
- Controllers assess card access without concern for the reader type.
- The reader transmits Wiegand data (1s and 0s) via a 5V pulse through Data 0 and Data 1 wires for processing.
RFID ATTACKS:
Understanding the Wiegand Protocol

Standard 26-bit Wiegand Format

- Upgrading legacy hardware and cards (PROX/iCLASS/Indala) is costly.
- The process is cumbersome, particularly for large facilities or campuses.
- Simultaneous upgrades may lead to a lockout, halting operations.
- Issuing new cards and updating every reader can cause business disruptions.
For these reasons, customers tend to adopt multiCLASS (SE) technology to reduce the upfront costs and complications.
RFID ATTACKS:
Deprecated Technologies
Why are there so many legacy readers?

RFID ATTACKS:
downgrade attacks
iCLASS SE/SEOS >> iCLASS legacy
- Majority of iCLASS SE readers support iCLASS Legacy
- An attacker can use iCLASS SE reader w/Standard Keys to capture the wiegand data
- Attacker uses an iCLASS 2k card and:
- Writes the compromised Facility Code & Card Number using a Proxmark3
- Disables encryption (altering a single bit in Block #6)
- Assuming that the facilities iCLASS SE readers have "Legacy Support" enabled the card will read
The controller does not care about the technology being presented. It only cares about the Facility Code and Card Number that are being presented.

RFID ATTACKS:
downgrade attacks [Multiclass (SE)]
iCLASS Legacy/SE/SEOS >> Prox/EM/AWID
- An attacker can use iCLASS SE reader w/Standard Keys to capture the wiegand data
- Attacker uses an T5577 card and:
- Writes the compromised Facility Code & Card Number using a Proxmark3
- Assuming that the facilities multiCLASS SE reader supports PROX/EM/AWID the card will work
The controller does not care about the technology being presented. It only cares about the Facility Code and Card Number that are being presented.

A company can significantly increase its security posture by implementing Elite keys instead of Standard keys. This will prevent non-client iCLASS SE readers from being able to capture the data.
RFID ATTACKS:
Preventative Controls
Elite Keys
OSDP
OSDP has recently hit the streets and aims to replace the Wiegand communication between readers and their controllers. While it touts unique encryption between each reader and the controller, some flaws still exist.

rfid Attacks:
(not so) longrange cloning

- Theatrical Range: 20-28 inches
- Actual Range: 4-7 inches
- Locate an effective choke point
- Maintain a non-threatening appearance
- Avoid attempting while in transit
- Follow the badge closely with the reader
- Consider targeting smokers
-
Adhere to the principle: Two is one, one is none.


rfid Attacks:
(not so) longrange cloning
Chokepoint Identification: Exterior of Facility

rfid Attacks:
(not so) longrange cloning
Chokepoint Identification: Interior of Facility




rfid Attacks:
(not so) longrange cloning
Tips for Success
- Bag placement relevance to card placement
- Employee Badge
- Your Access Card
- Single Operator Operations
- Chokepoints (in passing)
- Isolation
- Directions?
- Multiple Operator Operations
- Elevator Pinning
- Traffic Direction

Stealth Placement

- Opposite side of badged door
- Unlocked door with no reader
- Main/guest entrance
- Elevator w/o reader
- Latrine
- Try to be out of view of cameras
RFID Attacks: Card Skimming
Stealth Wiegand Data Interpreter

Application
- Already know the FC & CN range
RFID Attacks:
RFID Bruteforcing
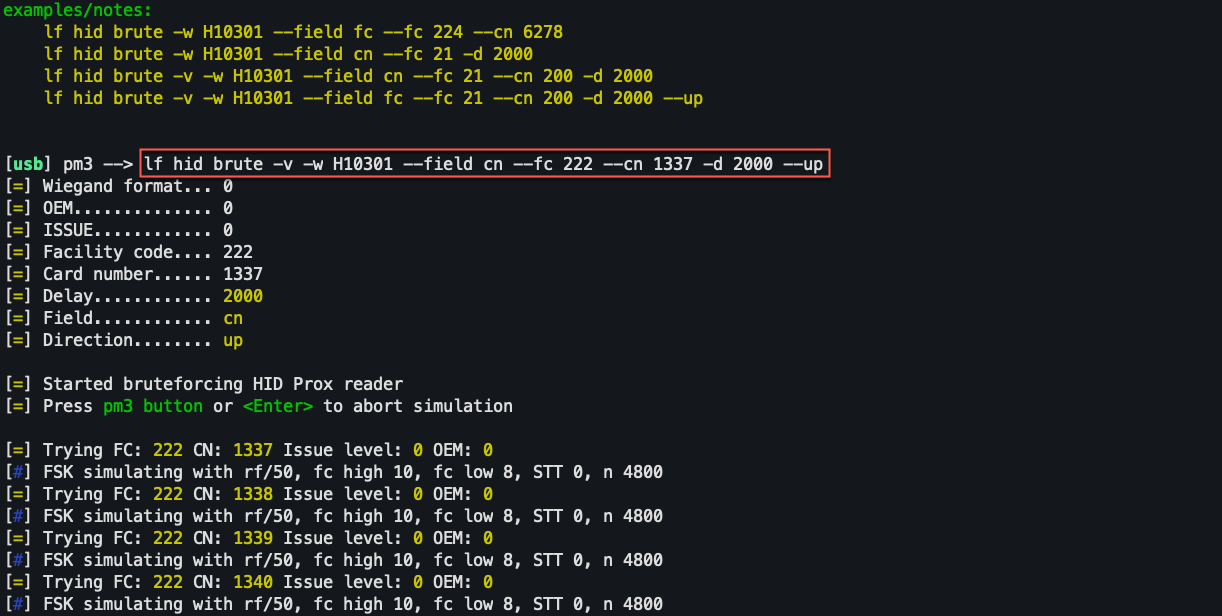
Reasons not to do it...

RFID Attacks: RFID Bruteforcing
Writing Captured Card Data
writing captured card data: hid Prox
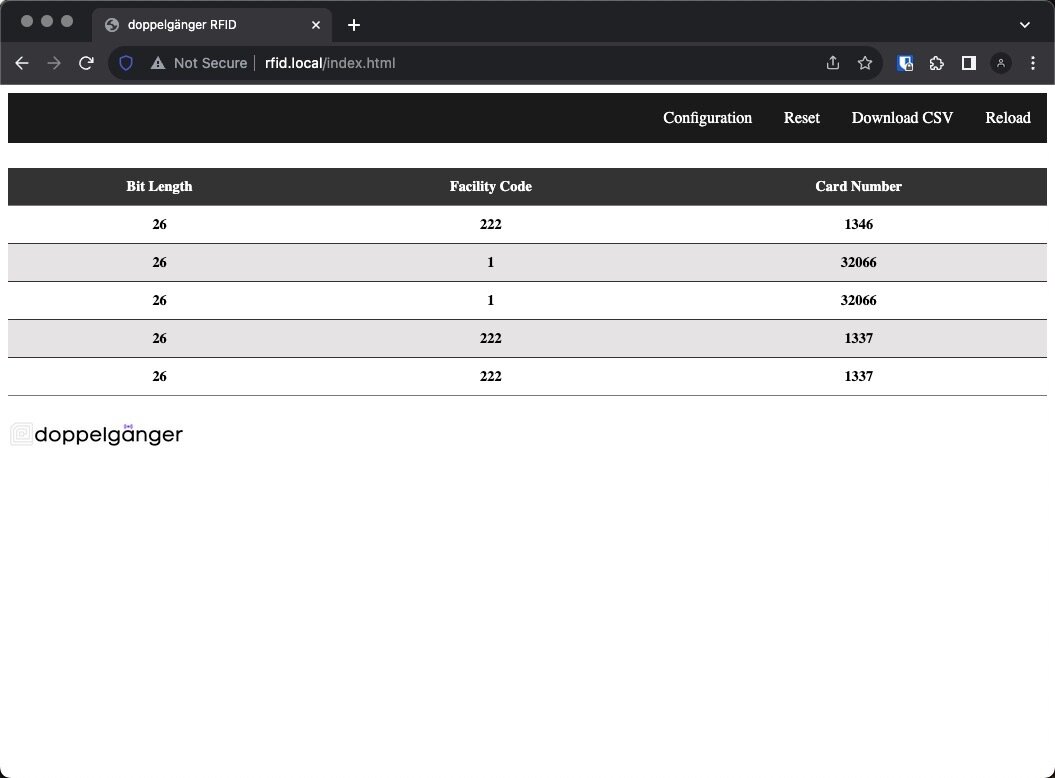
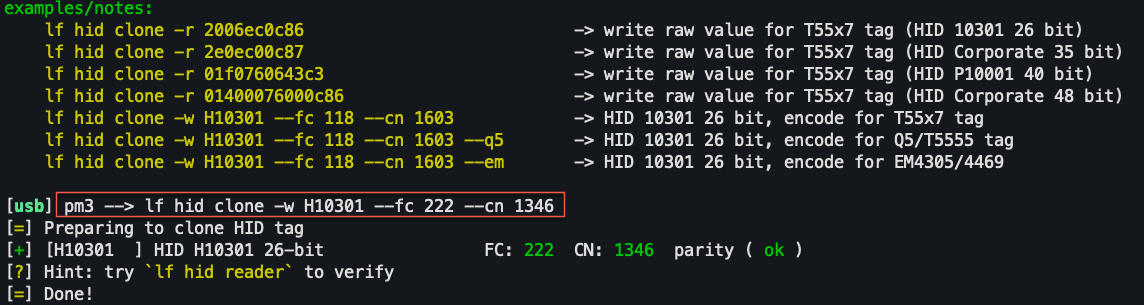

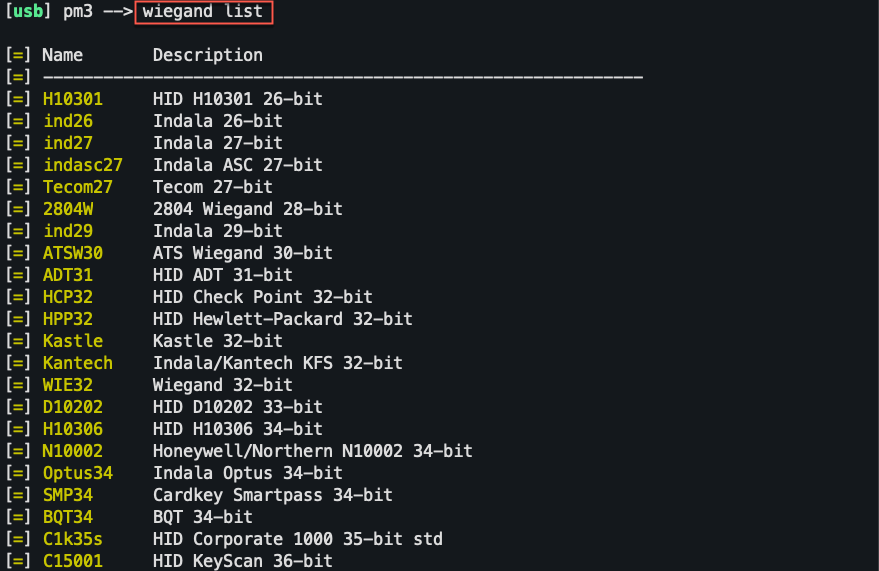
writing captured card data:
wiegand list

writing captured card data:
Indala

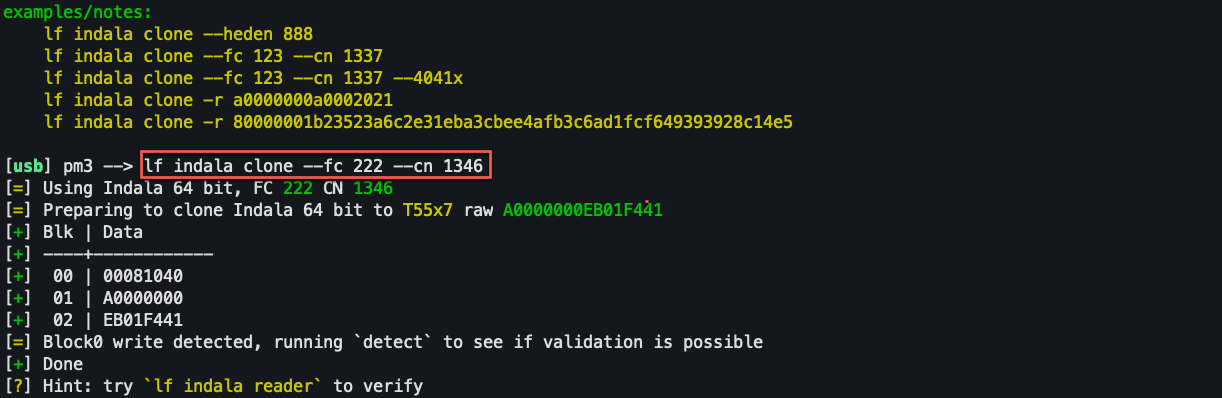

writing captured card data:
iclass (SE/SEOS)
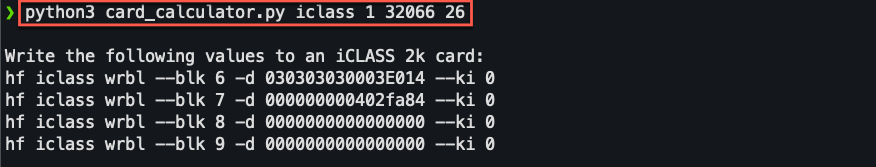
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tweathers-sec/useful_physical_information/main/card_calculator.py
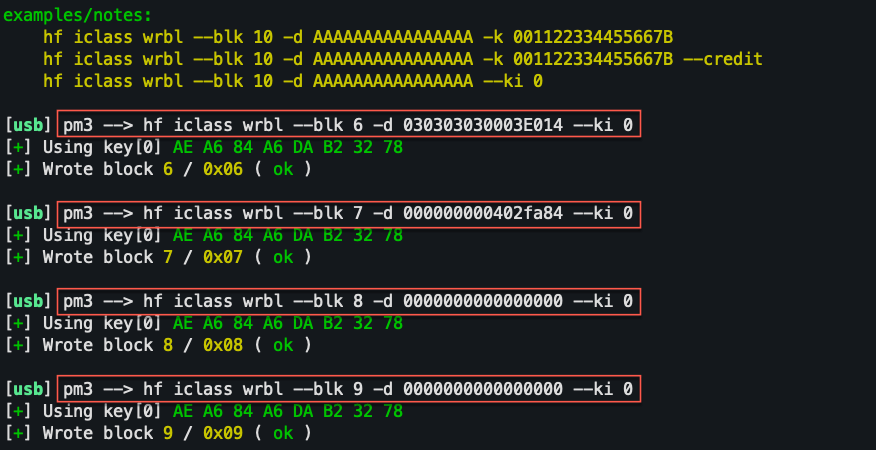

writing captured card data:
iclass verify data
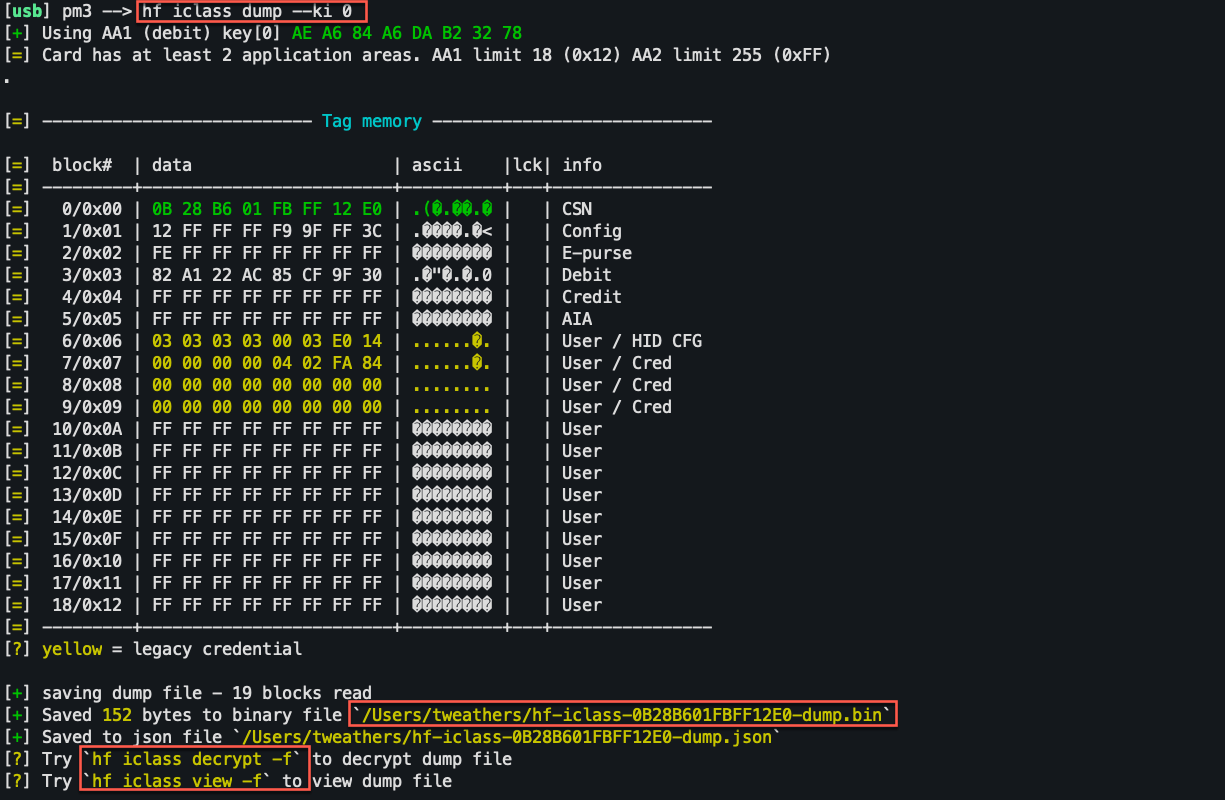

writing captured card data:
ICLASS VERIFY DATA
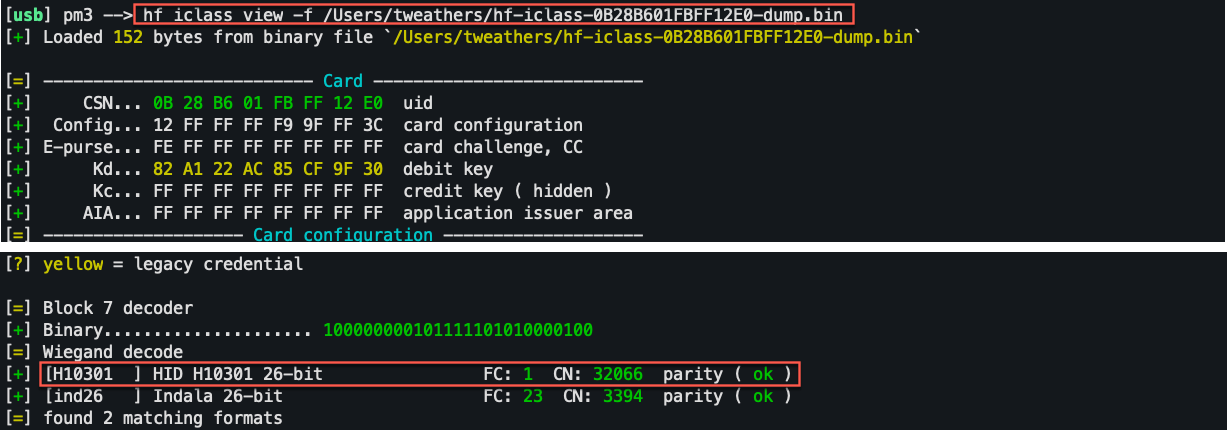

writing captured card data:
doppelganger Assistant
QUESTIONS?
PLUG
Three Days / Tampa, FL
- Pre-sales & Authorization
- Remote Reconnaissance
- Digital Surveillance
- Surreptitious Entry Tactics
- Badge Cloning & Replication
- Post-Exploitation
- Live Facility Breach Exercise
Upcoming Dates (2024):
October 16 - 18
PRIVATE CORP. & GOVERNMENT TRAINING AVAILABLE


PPE Course Highlights
Mobile Recon


PPE Course Highlights
Lockpicking & Dumpster Diving

PPE Course Highlights
Facility Access


PPE Course Highlights
Post Exploitation


PPE Course Highlights
Mission Complete


DEMO
Longrange Cloning
Demo Stations

Static Analysis
Writing Cards
Installing PM3
- Assess real-world read range
- Configure Doppelganger
- Write Card Data
- Analyze Cards / Device Setup
- Write Card Data
- Write Captured Cards
- Doppelganger Assistant
- Iceman Proxmark3
Stealth / MFAS
- Place Device
- Capture Reads
- Write Card Data
https://physicalexploit.com/docs/products/getting-started/
Documentation


Badge Cloning: A Penetration Tester's Guide to Capturing and Writing Badges
By mwgroup
Badge Cloning: A Penetration Tester's Guide to Capturing and Writing Badges
Learn about badge cloning and RFID attacks from experts Travis Weathers and Ralph May. Discover the vulnerabilities in RFID technologies and how to protect against them through demonstrations and discussions.
- 877







